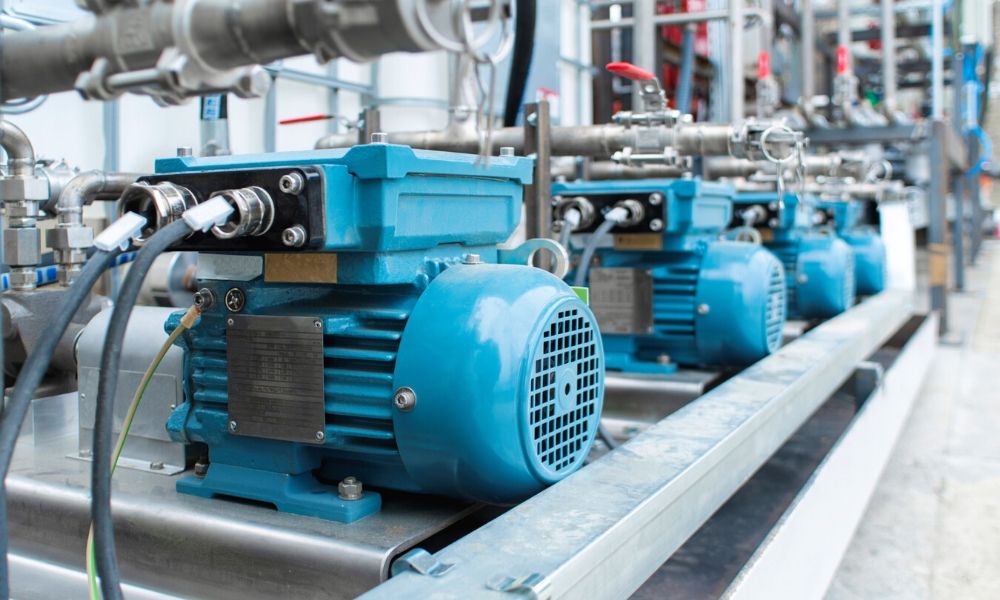
Modern industry relies on precision movement and controlled power delivery across countless applications. From conveyor systems to automated machinery, the ability to convert electrical energy into mechanical motion is at the heart of many operations. Selecting the right type of motor involves understanding how different technologies support specific performance requirements, environmental conditions, and long-term maintenance goals. With a range of motor solutions available, it’s important to match the most suitable product to your system needs.
The Role of Electric Motors in Industrial Systems
Electric motors are essential components that generate rotational force (torque) from electrical input. They serve in applications such as pumps, fans, robotic arms, packaging systems, material handling, and more. Motors vary in size, power output, and design, tailored to different loads and operating conditions. Understanding motor characteristics helps businesses optimise performance and energy efficiency while reducing downtime and service costs.
Types of Motors and Their Applications
There are several types of motors, each suited for specific functions:
AC Motors (Alternating Current)
Common in fixed-speed and variable-speed operations where reliability is key. AC motors are often used in HVAC systems, compressors, and industrial fans.
DC Motors (Direct Current)
Valued for precise speed control and variable torque capabilities. DC motors are frequently found in battery-powered systems, automotive components, and adjustable applications.
Servo Motors
Designed for high-performance motion control with feedback systems. They are prevalent in robotics, CNC machinery, and automation that requires accurate positioning.
Stepper Motors
These motors move in incremental steps and are useful where precise control is necessary without feedback, such as in 3D printers and small automation systems.
Each motor type has specific strengths, and choosing the right one depends on the desired balance between speed control, torque requirements, and system complexity.
Understanding Gear Integration
Many industrial systems require not just rotational motion but controlled torque and speed. This is where the integration of motor and gearing becomes critical. By adding gearing elements to the motor, the output speed can be reduced while increasing torque, allowing machines to perform heavy-duty operations without overloading the motor.
A unit that combines a motor with gearing functionality provides smoother motion at customised output speeds, making it ideal for applications such as automated lifts, conveyors, and precision handling systems.
Key Considerations in Motor Selection
When selecting a motor for industrial use, consider the following:
Power Requirements
Determine the necessary power output based on load size, expected duty cycle, and operating conditions.
Speed and Torque Characteristics
Understand whether constant speed, variable speed, or high torque at low speeds is needed for your application.
Control Requirements
Some systems require advanced control features such as feedback loops or integration with PLCs (programmable logic controllers).
Environmental Factors
Consider whether the motor will operate in conditions involving dust, moisture, temperature extremes, or corrosive elements.
Maintenance and Longevity
Select motors known for durability and ease of service to minimise downtime.
These factors ensure that the motor performs reliably within its application environment.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Energy efficiency is a key consideration, especially in continuous production environments. Motors that operate efficiently reduce electricity costs and contribute to overall sustainability goals. High-efficiency motors may have a higher upfront cost but often deliver savings over time through reduced energy consumption and lower operating temperatures.
Installation and Configuration
Proper installation ensures efficient performance and maximises the motor’s lifespan. Mounting position, alignment with mechanical loads, and appropriate grounding are all critical aspects. In more complex systems, configuration may also involve integrating the motor with drives, controllers, and feedback sensors.
Technicians often rely on manufacturer documentation and guidelines during installation to meet safety and performance standards.
Maintenance Best Practices
Routine maintenance improves reliability and prevents unexpected breakdowns. Essential tasks include:
- Checking lubrication levels for bearings
- Inspecting electrical connections for tightness
- Monitoring vibration and temperature changes
- Cleaning dust and debris from ventilation areas
Scheduled maintenance helps identify issues early, reducing repair costs and production interruptions.
Matching Motors to Application Needs
Different industries have varied motor requirements. For example:
- Manufacturing plants: Continuous duty motors with robust construction
- Packaging lines: Motors with precise control and quick response
- Material handling systems: High torque and durable output stages
- Automation: Compact motors with integrated control features
Understanding the specific demands of your application streamlines the selection process and improves system performance.
Safety and Compliance
Industrial environments often require adherence to safety and electrical standards. Motors and associated components should meet relevant certifications for safe operation. This is particularly important in sectors such as food processing, hazardous environments, or high-voltage systems.
Safety enhancements may include protective guards, emergency stop mechanisms, and grounding practices that protect both personnel and equipment.
Integrating Motors with Control Systems
Motors frequently operate as part of larger automated systems where control precision is crucial. Integration with control systems such as PLCs allows for programmable operation, coordinated motion, and feedback-driven adjustments. This level of control enhances efficiency and enables complex tasks to be executed with consistency.
Future Trends in Motor Technology
Advances in motor technology continue to improve performance, efficiency, and integration. Innovations such as brushless DC motors, smart sensors, and digital drive integration enhance reliability and support predictive maintenance. These technologies also help reduce downtime and enable real-time monitoring of motor health.
Keeping abreast of industry trends helps businesses adopt solutions that match future operational needs.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Choosing the right motor for your application involves a careful assessment of power needs, control requirements, environmental conditions, and long-term objectives. By considering these elements and consulting reliable product ranges — including quality gear motors and electric motor options — you can ensure your system performs effectively and efficiently.